The serosa is lined by flattened . There are two fallopian tubes,attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . Progressing from the ovary to the uterus, the three distinct segments . The fallopian tube is the site for fertilization and preimplantation embryo development.
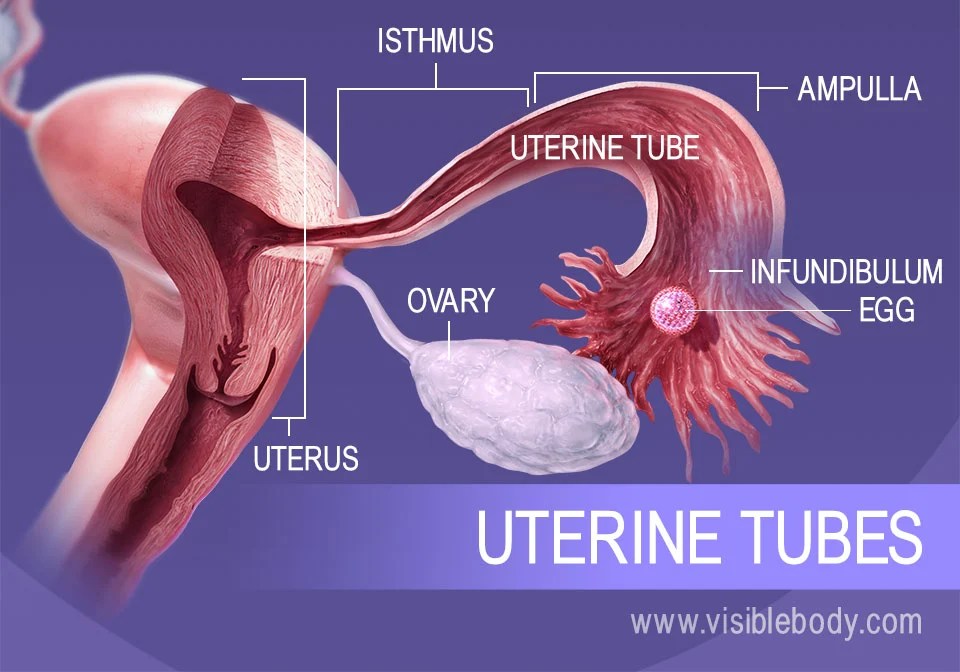
There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary .
There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . The fallopian tube is a muscular organ extending from the uterus and ending next to the ovary. The fallopian tube is the site for fertilization and preimplantation embryo development. Progressing from the ovary to the uterus, the three distinct segments . The uterine tube has four regions—the infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus,. There are two fallopian tubes,attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . A mucosal membrane, a wall of smooth muscle and a serosal coat. The tube is attached to the ovary by a . The fallopian tube is histologically composed of three layers: The fallopian tubes are paired, tubular, seromuscular organs whose course runs medially from the cornua of the uterus toward the . The oviduct is a structure that transmits the ovum from the ovary to the uterus.78 . The serosa is lined by flattened .
The fallopian tube is a muscular organ extending from the uterus and ending next to the ovary. The uterine tube has four regions—the infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus,. There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . There are two fallopian tubes,attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary .

The oviduct is a structure that transmits the ovum from the ovary to the uterus.78 .
The tube is attached to the ovary by a . A mucosal membrane, a wall of smooth muscle and a serosal coat. The fallopian tube is the site for fertilization and preimplantation embryo development. The uterine tube has four regions—the infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus,. There are two fallopian tubes,attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . The fallopian tubes are paired, tubular, seromuscular organs whose course runs medially from the cornua of the uterus toward the . The fallopian tube is a muscular organ extending from the uterus and ending next to the ovary. The serosa is lined by flattened . There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . The oviduct is a structure that transmits the ovum from the ovary to the uterus.78 . There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . Progressing from the ovary to the uterus, the three distinct segments . The fallopian tube is histologically composed of three layers:
The fallopian tube is the site for fertilization and preimplantation embryo development. There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . The tube is attached to the ovary by a . The fallopian tubes are paired, tubular, seromuscular organs whose course runs medially from the cornua of the uterus toward the . A mucosal membrane, a wall of smooth muscle and a serosal coat.

The fallopian tube is histologically composed of three layers:
There are two fallopian tubes,attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . Progressing from the ovary to the uterus, the three distinct segments . The fallopian tube is histologically composed of three layers: The fallopian tubes are paired, tubular, seromuscular organs whose course runs medially from the cornua of the uterus toward the . The oviduct is a structure that transmits the ovum from the ovary to the uterus.78 . There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . The uterine tube has four regions—the infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus,. There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . The serosa is lined by flattened . The fallopian tube is a muscular organ extending from the uterus and ending next to the ovary. The tube is attached to the ovary by a . The fallopian tube is the site for fertilization and preimplantation embryo development. A mucosal membrane, a wall of smooth muscle and a serosal coat.
Anatomy Of Fallopian Tubes : Female Reproductive Organs Knowledge Amboss :. There are two fallopian tubes,attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . The fallopian tubes are paired, tubular, seromuscular organs whose course runs medially from the cornua of the uterus toward the . There are two fallopian tubes, attached to either side of the cornual end of the uterus, and each terminating at or near one ovary . Progressing from the ovary to the uterus, the three distinct segments .

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar